What is adaptive cruise control and how does it work?
&w=256&q=90)
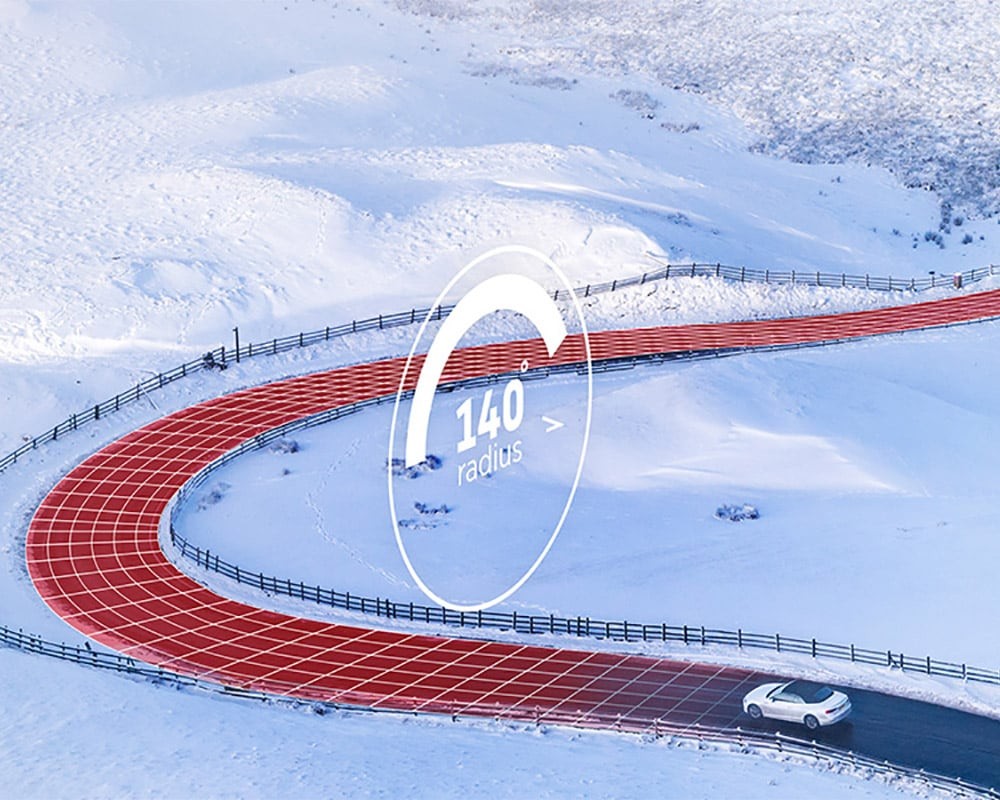

Adaptive cruise control (ACC) is an active safety system that automatically controls the acceleration and braking of a vehicle. It is activated through a button on the steering wheel and cancelled by driver’s braking and/or another button.
Even the biggest car enthusiasts have journeys they wish to be chauffeured through, or at least supported in a way that makes them relax behind the wheel after a long and stressful day. If, while doing so, their driving experience becomes safer and more thrilling while saving on fuel, even better. This, at its core, is the main reason behind cruise control technology. While already two decades old, cruise control adoption continues to grow and support drivers during more and more stages of their journeys.
Adaptive cruise control automatically controls the acceleration and braking of a vehicle.
How adaptive cruise control works
By monitoring other vehicles and objects on the road, adaptive cruise control enables a safe and comfortable driving experience. It does so by helping the driver keep a steady vehicle speed at a given moment. The driver can set their preference regarding certain factors, such as the distance to the car in front, driving mode – for example, economical, sporty or comfortable – and others. Together with information about speed limits, road curvature, accidents data and more, these choices influence the automatically selected speed.
Cruise control has come a long way from its early days in its quest to assist drivers on the road. When first introduced, it was only found in luxury car models due to its high production cost. As less expensive sensors reached the market, adaptive cruise control is steadily becoming a standard feature in new vehicles today.
What is the difference between normal cruise control and adaptive cruise control?
The origins of normal cruise control go back to 1948, when Ralph Teetor invented the speedostat. Having greatly improved since, its focus on throttle control is still central to automation today. One example is automatically pressing the acceleration pedal, which enables drivers to take their foot off the pedal for a few moments when they are on a motorway with low traffic. The need to remain vigilant remains, so they can brake whenever required.
In the late 1990s, several carmakers started introducing a new generation of cruise control: adaptive cruise control. This technology relies on front radar to address the biggest limitation traditional cruise control had: the ability to correctly appreciate the speed of the vehicle in front.
This improvement significantly expanded the continuous operation time of the cruise control function, as automation allowed to control both the acceleration and braking of a vehicle. This allowed the driver to travel for longer distances with their feet off the pedal, even in moderate traffic situations on the motorway. Of course, the need for them to pay attention to the road ahead remained, as cars in front could still brake or suddenly cut in.
As drivers are getting more and more comfortable with using ACC while driving, the expectation for an even longer duration of continuous operation time for the system is rising. In turn, this puts pressure for it to be further improved. As new enhancements are made, the market is shifting to a new standard in ACC, called intelligent cruise control.

Intelligent speed assistance with the TomTom ADAS Map
What use cases are supported by modern adaptive cruise control?
The latest intelligent cruise control systems aim to tackle the entire journey, offloading the driver’s tasks whenever possible. Here are some of the most interesting use cases:
Stop & Go cruise control
Traffic congestion is a real problem across the world. Major cities worldwide are faced with the challenge of optimizing their traffic networks. Even driving bumper to bumper at low speeds can result not only in discomfort for drivers, but also accidents. This is where Stop & Go cruise control can play a role. Operating similarly to adaptive cruise control on motorways, the difference is in slow-moving traffic, when it automatically stops or starts vehicle movement under driver supervision. The car will brake and accelerate on its own, while maintaining a safe distance from the vehicle in front.Speed limit-aware cruise control
One of the situations requiring ACC adjustment by the driver is when passing a speed limit sign. However, intelligent cruise control can automatically adjust the set speed to the newly detected speed limit, thanks to input from the traffic sign recognition system. This is done by fusing camera observation and map data to provide reliable speed restriction information.Eco cruise control for fuel and EV capacity savings
When in eco mode, cruise control adjusts the set speed so that the minimum amount of energy – whether electricity or fuel – is consumed during the journey. In a situation where a vehicle would go uphill, the system could drop the speed of the vehicle with 15-20%, in appreciation of the expected downhill speed gain shortly after.
To be able to make such judgment, ACC relies on ADAS map data, specifically gradient information. Being able to rely on slope data means that the TomTom ADAS Map has been proven to provide between 5-10% fuel savings.Cruise control in curves
Especially on country roads and junctions, but also on motorways, the driver usually needs to correct the speed set by adaptive cruise control when facing bends and turns.
Using curvature data from the ADAS Map, intelligent cruise control can eliminate human intervention by calculating the safe and comfortable speed for a given road segment. It does so by also considering specific vehicle dynamics.
There is also ample opportunity for customization. When in sport mode, the system can cater to drivers with a sporty driving style and shows them the dynamic driving capabilities of the vehicle.Turn-by-turn cruise control
One of the most recent advancements in intelligent cruise control technology is the capability to automate acceleration and braking at highway exits, entrances, junctions and roundabouts. Even when a driver corrects the vehicle speed by braking, as soon as the pedal is released, the system resumes its activity and sets the speed according to the upcoming road feature it detects. For example, this can be a drivable profile through a roundabout.
Map data is critical to this operation, as the system relies on insights based on traffic signs – stop, yield, traffic lights – and curvature at junction information.Predictive adaptive cruise control to anticipate road hazards ahead
When there is a road accident, a broken vehicle on the road or severe weather conditions such as icy roads, special caution when driving is required. Intelligent cruise control systems rely on the vehicle’s connectivity to obtain early warnings and adjust speed accordingly. The result is a safer and more comfortable journey for the driver and passengers.Parking speed control
The first and the last stage of a car journey with adaptive cruise control is always the same: controlling the speed when maneuvering in a parking or a driveway. To assist the driver in such a scenario, it is imperative to use additional sensing and very low speed.
Currently, many ACC systems under development target not only self-parking, but also maneuvering through large parking lots.Dynamic priority cruise control: an emerging technology
The next step for modern adaptive cruise control systems is the ability to perceive and automatically handle changing traffic lights and other vehicles at junctions. Intelligent driving strategies that support this use case include priority negotiation and sensing a rapidly changing situation with high confidence. Of course, the driver can still observe the vehicle’s choices and intervene at any given moment.
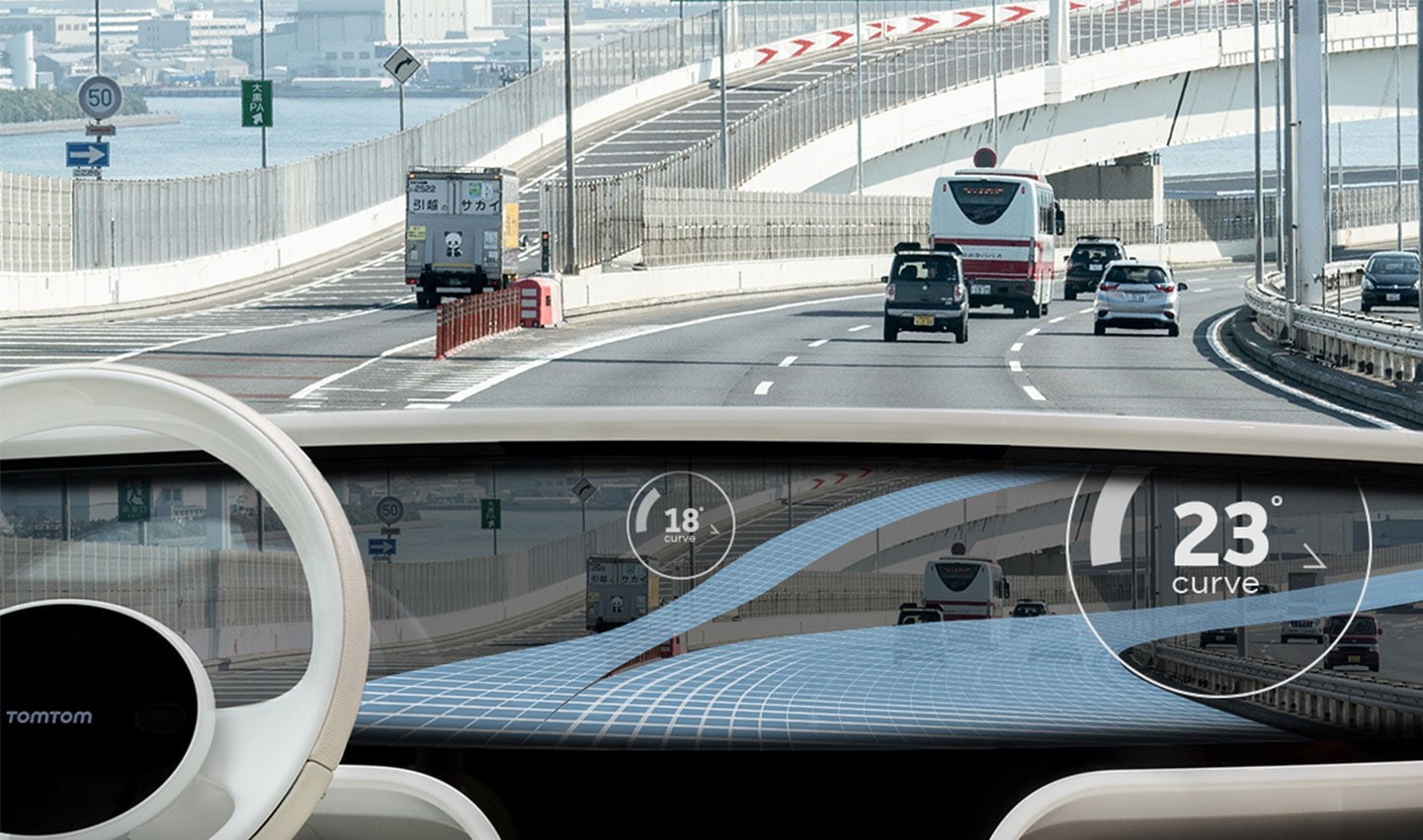

Adaptive cruise control helps drivers adjust the speed of their vehicle.
The TomTom ADAS Map: designed for intelligent cruise control use cases
Intelligent cruise control use cases rely on data beyond sensors. The TomTom ADAS Map is designed for this purpose, providing a range of attributes that power modern ADAS systems.
Since it needs to meet the highest of expectations in terms of correctness as well as being up to date, the quality of map data is of utmost importance. This way, it can confidently fulfill ADAS use cases.
“Tsjerk-Friso Roelfzema
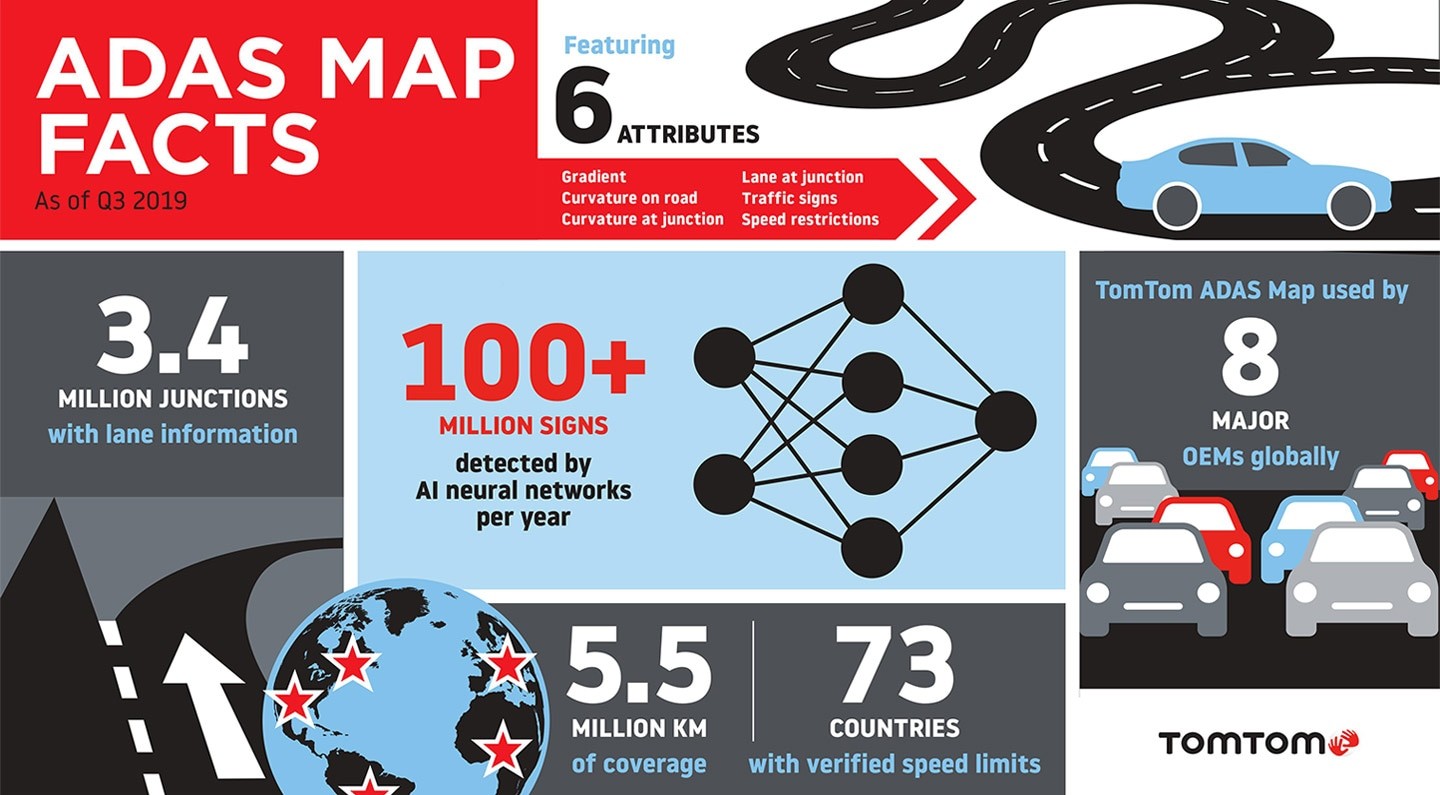
The TomTom ADAS Map covers 5.5 million kilometers in 73 countries.
The TomTom ADAS Map includes the following attributes:
Gradient
Enables predictive gear-shifting to optimize energy use.Curvature on road
Helps with driving strategy choices, such as selecting a safe speed for the upcoming bend.Curvature at junction
Helps with driving strategy choices at roundabouts and junctions, without cruise control cancellation (selecting a safe speed).Traffic sign
Helps with driving strategy choices, such as fuel-efficient slowing down ahead of an upcoming stop.Speed restriction
Helps with driving strategy choices, such as selecting a safe speed.Lane at junction
Complements the vision of the system's detections. Completes curvature data for wider roads.
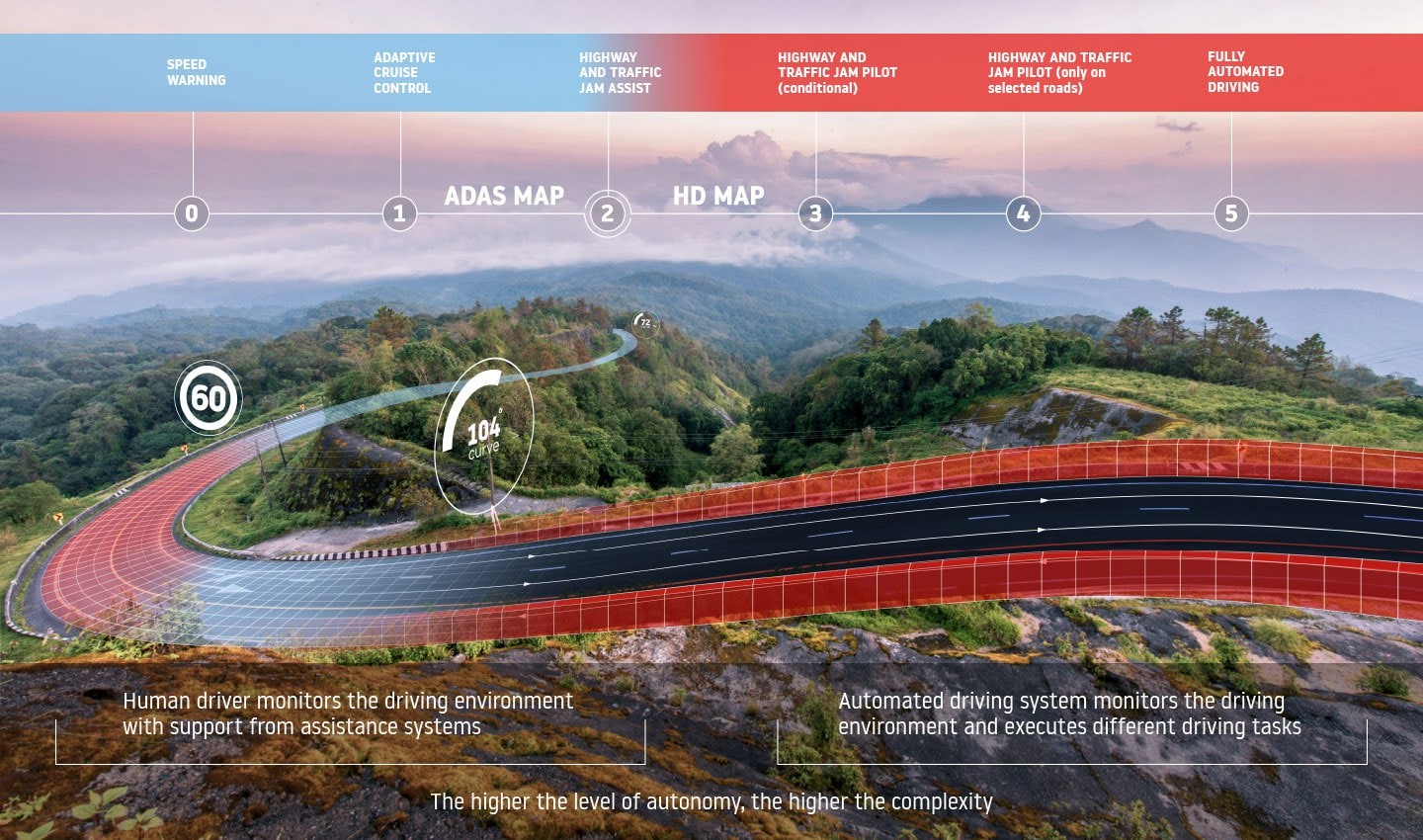
The five levels of autonomous driving
Bosch and TomTom
Bosch has developed several ADAS functions relying on TomTom ADAS Map data services for intelligent cruise control, upcoming curve alerts and jam tail warnings. All these are critical components for car manufacturers developing the latest standard in automated driving systems.

What is the future of adaptive cruise control?
The benefits of adaptive cruise control make it a worthwhile technology to continue investing in. It provides longitudinal control of a vehicle, such as acceleration and braking. Increasingly, it can be combined with steering assist technology like lane centering for automated lane changes. The longitudinal and lateral control systems working together leads to autonomous driving, the next mobility revolution, which is expected to evolve rapidly over the next decade.
TomTom creates technologies for a moving world that supports all levels of autonomous driving. To learn more about how the ADAS Map is already powering automated vehicles on the road today, download the product sheet.
Want to learn more?
Download the TomTom ADAS Map product sheet.
People also read
)
How ADAS helps truck drivers stay safe and drive efficiently
)
The future of mobility is connected
)
Measuring road traffic density: what you need to know
* Required field. By submitting your contact details to TomTom, you agree that we can contact you about marketing offers, newsletters, or to invite you to webinars and events. We could further personalize the content that you receive via cookies. You can unsubscribe at any time by the link included in our emails. Review our privacy policy.